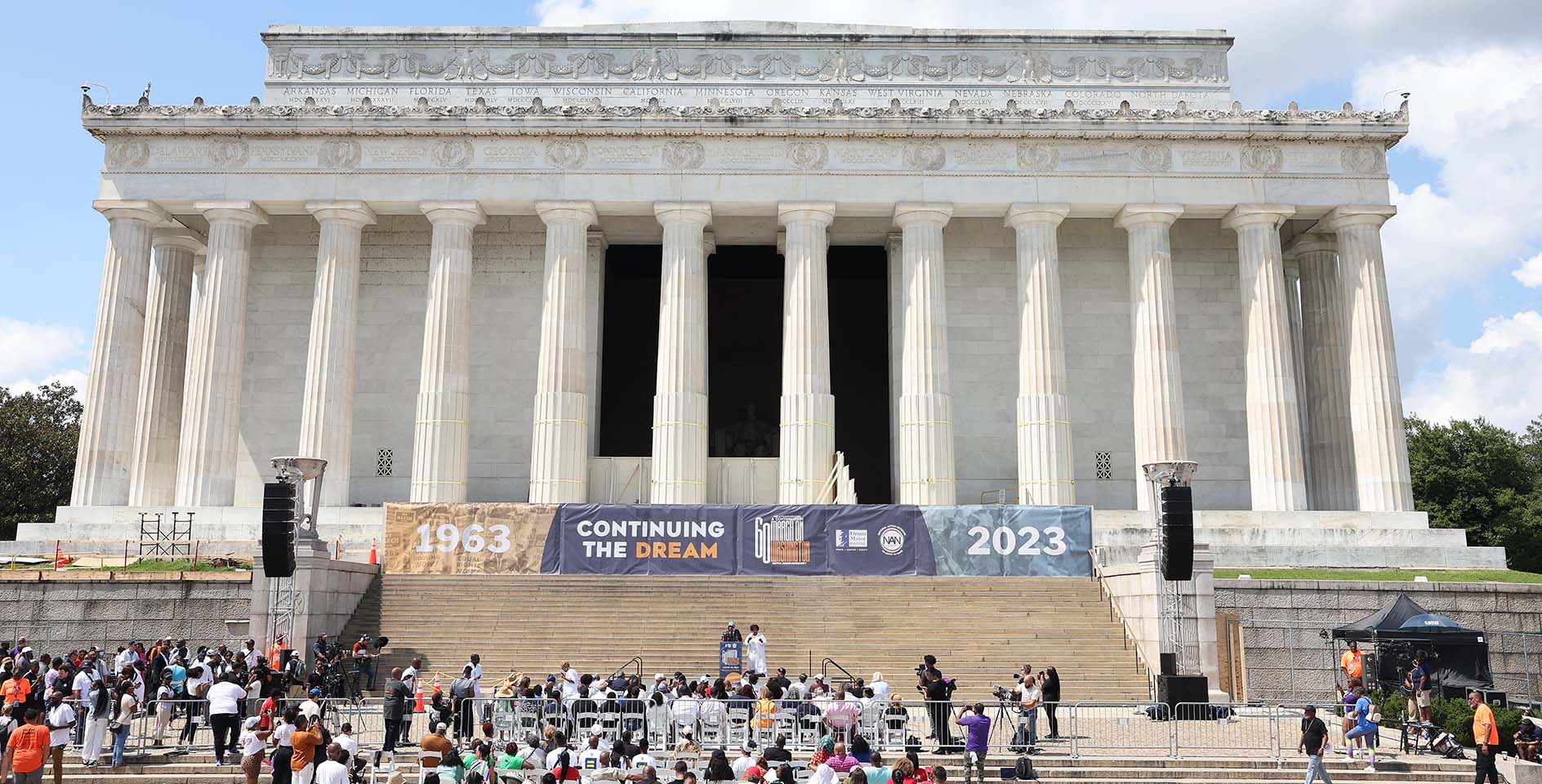
Monday marked the 60th anniversary of the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. Held on Aug. 28, 1963, the march stands as a watershed moment in the Civil Rights Movement, influencing civil rights legislation and contributing to the end of racial segregation.
Here is what you should know about the Christian significance of the march, its impact on civil rights laws, and the ongoing quest for racial reconciliation.
Historical context: A moral imperative to overturn Jim Crow
The March on Washington occurred during a tumultuous period characterized by racial discrimination and social unrest. Although slavery had been abolished, systemic racism persisted, particularly in the form of Jim Crow laws. Named after an offensive and degrading stereotype of African Americans, Jim Crow laws were a collection of state and local statutes that enforced racial segregation in the Southern United States.
One of the primary tenets of Jim Crow laws was the doctrine of “separate but equal,” upheld by the Supreme Court case Plessy v. Ferguson in 1896. This doctrine allowed for racial segregation so long as facilities were “equal,” though in reality, they were often inferior for African Americans.
Jim Crow laws also mandated the segregation of public schools, public transportation, restrooms, restaurants, and even drinking fountains. They entrenched racial boundaries by establishing voting restrictions and prohibiting interracial marriages. These laws often enforced job discrimination, ensuring that lucrative and desirable jobs were reserved for white individuals.
Jim Crow laws were enacted primarily from the late 19th century to the early 20th century and remained in effect at the time of the march. This struggle for civil rights was therefore not merely a political or social endeavor but a moral imperative deeply rooted in the Christian doctrine that all human beings are created in the image of God.
The march: A manifestation of Christian activism
Organized by civil rights and labor leaders like A. Philip Randolph and Bayard Rustin, the March on Washington brought together an estimated 250,000 individuals of all races. Many of the promoters and speakers at the events were Christian leaders, as were a great number of those who participated in the march.
Although the organizers disagreed about the purpose of the event, the group came together on a set of goals:
- passage of meaningful civil rights legislation;
- immediate elimination of school segregation;
- a program of public works, including job training, for the unemployed;
- a federal law prohibiting discrimination in public or private hiring;
- a $2-an-hour minimum wage nationwide;
- withholding federal funds from programs that tolerate discrimination;
- enforcement of the 14th Amendment to the Constitution by reducing congressional representation from states that disenfranchise citizens;
- a broadened Fair Labor Standards Act to currently excluded employment areas;
- and authority for the attorney general to institute injunctive suits when constitutional rights are violated.
Event organizer Bayard Rustin recruited 4,000 off-duty police officers and firemen to serve as event marshals and coached them in the crowd control techniques he’d learned in India studying nonviolent political participation. The official law enforcement also included 5,000 police, National Guardsmen, and Army reservists. No marchers were arrested, though, and no incidents concerning marchers were reported.
At the close of the event, Dr. Martin Luther King Jr., a Baptist minister, delivered his iconic speech from the steps of the Lincoln Memorial. King improvised the most recognizable, memorable part of the speech for which he is most famous, according to his speechwriter and attorney Clarence B. Jones. Although King had spoken about a dream two months earlier in Detroit, the “dream” was not in the text prepared by Jones. King initially followed the text Jones had written, but gospel singer Mahalia Jackson yelled, “Tell ’em about the dream, Martin!” King nodded to her, placed the text of his speech aside, and veered off-script, delivering extemporaneously what is referred to as the “I Have a Dream” speech, one of the most famous orations in American history.
A cultural shift and the end of segregation
The March on Washington was instrumental in the passage of key civil rights legislation.
- The Civil Rights Act of 1964, which outlawed discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin, echoed the biblical principles of justice and equality.
- Similarly, the Voting Rights Act of 1965 sought to eliminate racial discrimination in voting, aligning with the Christian conviction of fair treatment for all people made in God’s image.
Beyond legislation, the march initiated a significant cultural shift. The event brought the issue of racial inequality into the American consciousness, challenging people to confront their prejudices and to strive toward the Christian ideals of love, mercy, and unity. While laws could mandate desegregation, it was this change in collective consciousness that truly began to dismantle systemic racism.
As we reflect on the march, it’s essential to recommit to the Christian call for racial and ethnic reconciliation. The Apostle Paul writes in Galatians 3:28, “There is neither Jew nor Gentile, neither slave nor free, nor is there male and female, for you are all one in Christ Jesus.” This verse highlights the biblical mandate for unity, transcending all racial and ethnic divisions, especially in the Church.
The March on Washington serves as a profound reminder of the Christian principles of justice, equality, and love for one’s neighbor—all grounded in the reality that we are all created in God’s image. The event was not just a milestone in American history; it was a manifestation of Christian activism that led to transformative civil rights legislation and cultural changes. However, the journey toward racial reconciliation is far from over, as evidenced by the devastating and sinful acts of racial hatred and violence we see too frequently. As followers of Christ, we are called to continue this vital work, striving to build a society where all are equal, all are loved, and all have the opportunity to hear the good news of Christ Jesus.